Ethereum Classic (ETC), more often considered as a simple fork of the famous and well-known Ethereum company, is in fact the original blockchain of the latter. Ideological differences led to the creation of a fork that divided the members of the Ethereum community into two sides: on the one hand, the purists who wanted to keep and operate with the concept of invariability and transparency of the blockchain, and on the other, those who wanted a modernization that would solve some problems related to hijacking or other failures within the blockchain.
Since the split, these two twin blockchains have been subject to comparisons and each have their supporters, as well as their detractors.
What is Ethereum Classic (ETC)?
Ethereum Classic is the sister blockchain of the famous cryptocurrency, Ethereum (ETH), which follows Bitcoin in the market rankings. It was created in 2016 as a result of a fork, a very common process in the world of cryptocurrency that aims to solve problems that any blockchain may face due to disagreements within the company or other major system failures. This system refers to a fork, a division into several branches more concretely. In the world of cryptocurrency, this refers to the breaking of a blockchain into two different blockchains.
There are cases of hard fork, which means that there is a great divergence in the consensus rules and which often leads to a permanent separation of the chain, but also soft fork, which means that the changes made to a protocol have kept a certain compatibility with previous versions. In the case of Ethereum and Ethereum Classic, it is a hard fork that led to the creation of the sister blockchain of Ethereum. The objective of Ethereum Classic is to become in the future, an efficient and influent solution that would allow to connect the greatest number of devices in the world so that individuals can exchange contracts and values.
Ethereum Classic’s cryptocurrency is Ether Classic (ETC) and its tokens are used to pay the miners who take part in the development of the blockchain.
Under which circumstances was Ethereum Classic created?
In 2016, the DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization) venture capital structure launched a smart contract with the aim of sponsoring the decentralized applications of the ecosystem developed by Ethereum Classic: the Dapps. The transparency and the goals of this smart contract have facilitated the sale of DAO tokens, which have raised more than 150 million dollars in just a few weeks. However, the problem with this project was the termination of contracts with members. Indeed, in order to withdraw from the program, participants had to use the Split function which allowed them to get their ETH tokens back: but only after a period of 28 days. This delay was in itself the flaw in the system.
It was when the system was hacked that the majority of the Ethereum community, with the approval of the founders, went on to create the Ethereum Classic hard fork.
A hacker had attacked the funds of people wishing to leave the DAO and managed to steal about 50 million dollars worth of Ether (ETH). Thanks to the hard fork, Ethereum managed to return to the state of the blockchain before this theft occurred and thus recover and return to investors the capital they had invested with the company. This event marked the beginning of an ideological divergence between the members of the community because some considered this solution as being contrary to the code of ethics of decentralization. They continued to use the original blockchain while denying the characteristics of the new version (supporters of Ethereum Classic).
The company’s partnerships
Since the Ethereum Foundation is not on the side of Ethereum Classic, the company had to create a network of partners to continue its development. It engaged many partnerships with entities such as:
- ETC COOPERATIVE: responsible for the development and marketing of the ETC ecosystem.
- Ethereum Classic Consortium: in charge of promoting the ETC core values.
- IOHK: mathematics and algorithms specialist
- Ethereum Commonwealth: works on the blockchain and the Classic Ether Wallet.
- ETCDEV: engineers and developers working on blockchain
- ETC LABS: testing laboratory for ETC innovations
How does Ethereum Classic work?
The keyword of the Ethereum Classic company is invariability. No matter what the circumstances or events, the ETC blockchain must not be modified: “Code is law” (an ideology according to which a group cannot reform the path of the network in any way). Despite the various ideologies and views, the functionality of Ethereum and Ethereum Classic is very similar. The characteristics of the blocks and the rewards (mining) of the two chains are almost the same.
Ethereum Classic provides the ability to send money and values to others, as well as the ability to put invariable and secure smart contracts online. The company uses an open source blockchain and its EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine) network that allows it to run a multitude of scripts on a global scale and provides a standard mining based on the Ethash algorithm.
Ethereum Classic makes use of the Turing Complete programming language that allows developers to create and run decentralized applications, as well as issue new blockchain-based crypto-currencies. The network relies on virtual machines to support smart contracts and also has an optimized virtual machine, called SputnikVM, which allows for the enhancement of the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) for devices with lower power consumption.
The Proof of Work
This protocol uses proof-of-work validation to secure operations. The energy used by the machine is quantified and allows to determine which computers (individuals) can have access to privileges. New blocks are created every 15 seconds on the Ethereum Classic network. However, the number of participants in the blockchain makes the mining of tokens more and more time-consuming and complex; the energy spent on mining therefore increases continuously. That’s why some miners gather to form groups called “pools” and merge their energy and computing power in order to collect more tokens and share them among themselves.
Here are some mining pools you can join:
- ClassicPool
- MinerGate
- Epool
- Europool
- ETC-Poolcrypto
- Comining
- 91 Pool
- 2 Miners
In addition to proof of work, there is also the concept of proof of stake, which is used by other cryptocurrencies, including Ethereum Classic’s first competitor, Ethereum (ETH).
The Proof of Stake
As for the Ethereum branch, it is based on a process affiliated with the DASH blockchain, which is none other than the proof of stake. This program works thanks to a masternode, a connected computer that holds a copy of the entire blockchain system. To be a masternode, the individual must have a certain amount of tokens in his possession. He then has access to certain privileges and receives rewards in tokens, but also adapted transaction fees: this is the notion of staking.
Smart Contracts
The concept of smart contract was created in the 1990s by the cryptographer Nick Szabo. A smart contract is a computer protocol that directly executes a contract between two or more actors when the conditions required for its execution are met and honored. It works in the same way as a traditional contract except that, unlike a traditional contract, its execution is not governed by any legal authority and it does not require the intervention of any trusted third party.
The advantage of smart contracts is that they are less expensive, faster, and less complex to manage than traditional contracts.
Characteristics of Ethereum Classic (ETC) and Ethereum (ETH)
Ethereum (ETH)
Ethereum is a blockchain protocol created in 2015 by the young Canadian developer, Vitalik Buterin. It is a computing platform that allows the development of decentralized applications. The Ethereum network is considered to be a “global computer” or a “super computer”, especially because of the large number of interconnected computers that communicate constantly in order to make it work. Unlike Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies that operate on a peer-to-peer basis, Ethereum makes decentralized applications programmed by thousands of developers available to large companies in various sectors such as real estate, insurance, entertainment and finance.
Ethereum’s philosophy is based on the ideology of decentralization of financial institutions. Decentralized finance (DeFi) is a project of an open, global financial system built for the Internet age – an alternative to a system controlled and maintained by decades-old infrastructure and processes. To date, tens of billions of dollars in cryptocurrencies have enabled the funding and development of DeFi applications .
Today, the community of developers serving the Ethereum blockchain is one of the largest in the world: their work is well rewarded as Ether (ETH) is second in the cryptocurrency market behind the famous leader, Bitcoin.
Differences et similarities
The differences between the initial blockchain and its fork are not numerous, since on the one hand the blocks of each of the two branches are identical until block 1920000. There are therefore more similarities, especially in terms of tools such as smart contracts and Dapps, as well as the coding of the blockchain and the rewards that miners receive for their work.
However, since the division of the initial blockchain, depending on the ideologies of the different sides, differences have begun to appear within each branch, which has resulted in the emancipation and independence of each of the two blockchains:
- Ethereum Classic, for example, decided to keep using the Proof of Work protocol, while Ethereum now uses the Proof of Stake Protocol.
- Ethereum has the ability to produce infinite tokens, unlike its twin, which has a ceiling of between 210 and 230 million.
The advantages of Ethereum Classic
Here are in details, the pros of the Ethereum Classic blockchain and its ETC token:
- Decentralization: thanks to its Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), decentralized applications (Dapps) serving the item innovation sector (IOT) and smart contracts do not require the intervention of intermediaries or even central authorities.
- Speed of transactions: transactions are automatically verified, so they are processed and executed as quickly as possible.
- Invariability: all transactions cannot be modified or deleted once they have been entered into the blockchain database. It is because of a modification of the Ethereum blockchain that Ethereum Classic was created as a fork.
- The possibility of programming: one of the fundamental advantages offered by the Ethereum Classic blockchain. It is programmable, which allows developers to create and work on applications and smart contracts.
The controversies around Ethereum Classic
Ethereum Classic is often considered as a simple fork of Ethereum. Its low notoriety as well as its delay in development due to a lack of resources and its low level of security make this blockchain the target of controversy and criticism from Ethereum supporters.
The main teams and technologies have sided with Ethereum, Ethereum Classic has less potential to develop its network:
- Pioneer developers have sided with the other branch
- The project is seen as a clear opposition to Ether
- The company does not have the human resources necessary for its development
- The migration of mining power to Ethereum has put the company’s security at risk
Ethereum Classic has also experienced, numerous times, attacks from malicious hackers. In August 2020, the blockchain suffered 3 attacks from the 51% in the space of just one month. The last attack caused the modification of more than 7000 blocks and the first two caused the reorganization of 3693 blocks and 4000 blocks respectively.
What is a 51% attack?
A 51% attack, also known as a double-spending attack, is a reorganization of a blockchain by malicious individuals. By taking over a significant portion of the validation power, they are able to reorganize the chain in order to remove a payment that has been made while keeping the asset acquired in the transaction and retaining their cryptocurrencies. This kind of attack is more frequent in chains that use the Proof of Work method, such as Ethereum Classic where the different blocks are validated by mining, and are therefore less frequent in chains that use the Proof of Stake.
The double-spending attack is divided into 3 stages :
- The purchase of an asset: the hacker buys an asset when he holds a large amount of computing power of a network linked to a cryptocurrency and a large amount of tokens.
- The mining of a parallel chain: when the transaction, apparently legitimate for the acquisition of the good, is carried out, the hacker makes appear another transaction known as fraudulent in the chain of blocks which spends the same amount as the first and thus brings back the funds towards their origin. At the same time, he creates a parallel chain that is not visible to the rest of the network and on which the funds are transferred to his address.
- Reorganization of the chain: after the purchased goods has been delivered to him, he reveals the parallel chain to the network when it becomes longer than the chain where the legitimate transaction is located because of the computing power he holds. The reorganization of the chain occurs when the transaction present in the invalidated blocks of the first chain is put back in the mempool (waiting area for transactions in a blockchain) and the new blocks are validated.
The consecutive attacks against Ethereum Classic have strongly questioned the network’s security and shaken people’s confidence in the blockchain. It is therefore not impossible and even very likely that Ether Classic (ETC) will be removed from the listing of some exchange platforms.
Ethereum Classic’s various strategies to get back on its feet
To overcome its current flaws and failures, the company had taken the initiative to implement different measures, over several time periods.
Right now, Ethereum Classic had chosen to strengthen the cooperation of miners in the hope of keeping the Hashrate (hash rate, used to measure the computing power of a device) at a reasonable level. In addition, Ethereum Classic Labs planned to improve the supervision of the system in order to detect singularities and unusual changes in the hash rate more quickly, while the section in charge of development was advancing on the “Permapoint” project; a system whose mission would be to prevent chain reorganizations by hackers or any other person. In the long run, the team was considering integrating the PirlGuard protocol which would double the cost of double-spending attacks since malicious miners will come across mined “penalty blocks” when they have the idea to reorganize a blockchain. These require more resources to be mined and therefore will represent a hindrance to hackers’ actions.
On the other hand, Ethereum Classic was planning its separation from the Ethash algorithm in order to make it more complex to rent Hashrate on platforms, but also to differentiate itself once again from Ethereum (ETH) which uses the same algorithm. This separation should happen when the hard fork of Ethereum Classic would be ready and functional. The company was considering a migration to algorithms like Keccack-26 or Random X. More oriented towards the use of Keccack-26, the community felt that this algorithm could make ETC independent and allow it to reach a leading position in terms of hashrate of its own mining algorithm. The use of the Random X algorithm was less considered because it would not have been able to solve, as a whole, the difficulties that Ethereum Classic faces.
Despite the search for independence and the desire to distinguish itself from its twin Ethereum, the Ethereum Classic Labs, affiliated with Ethereum Classic, said it wanted to build a project in collaboration with the company Metronome that would serve as a bridge between the two blockchains: a project of interoperability. A first hard fork named Atlantis served as a base for this project while waiting for the implementation of the new hard fork nicknamed Agharta.
Agharta, the new Ethereum Classic hard fork
The Agharta project was started in January 2020. After its launch, the ETC tripled in value and reached the 5 dollar mark, and some time later (end of February) it sold at a price exceeding 9 dollars. The activation of the Hard fork has had a strong impact on the price of Ether Classic, but this evolution is also linked to the partnerships accumulated by the company at the same time. This project aimed to make Ether Classic users compatible with Ethereum in order to bring the two communities closer together.
The interoperability between the two branches has allowed Ether Classic to spread among Ether users and increase the use and acceptance of ETC tokens among individuals and especially businesses around the world.
The main companies that use and accept ETC tokens are the following:
- Crypto-games: an online gaming site that accepts cryptocurrency payments
- 1xBet: the famous sports betting company
- Smarty Scripts – a software development company
- Snel.com: a domain provider in the cloud world
- Mineshop: an IT company based in Ireland
Invest in Ether Classic
Should I invest? Is it a good investment? These questions always come up when discovering any cryptocurrency on the market. There are no sure things due to the volatility of cryptoassets and predictions made today about any cryptocurrency, whether positive or even negative, may prove to be wrong in the near future.
Therefore, no player can be sure of reaping profits on their initial investment or seeing the value of their chosen cryptocurrency increase.
How to get Ether Classic?
There are several options for purchasing ETC tokens.
Buying Ether Classic
Of course you can buy ETC tokens on platforms such as :
- Kraken
- Binance
- Coinbase
- eToro
- Wirex
- Libertex
There are a multitude of other buying platforms besides these. The choice is yours. However, before entering your payment information on a site, it is imperative that you research the site, consult reviews and make comparisons with other sites to determine which is the most appropriate for the currency you are looking for and the most reliable in terms of security.
Mining ETC tokens
Just like the majority of cryptocurrencies, it is possible to obtain them through mining. Mining consists of acquiring a great deal of computing power in order to solve mathematical calculations, the result of which is the validation of transactions. Miners receive a number of tokens depending on their speed but also depending on the number of tokens issued by the company of the chosen cryptocurrency. The rewards are then lower and lower when the company has an emission ceiling and requires more computing power.
It is also necessary to have the Ethminer software or the Claymore Dual Ethereum software on your computer system to be able to mine ETC tokens. The quality of the machine also plays a crucial role in this process, which is why it is important to have the necessary resources (quality hardware) to perform this task (there are specialized components for mining, such as Asics graphics cards). Technically, miners perform separate operations for each block thanks to a hash function that randomly generates strings. They then receive the tokens when the nodes examine the requested transaction.
Trading Ether Classic
Finally, you also have the option of using cryptocurrency trading to obtain Ether Classic. It is however advised to check that the platform you are on is reliable and secure as many losses/thefts of crypto assets take place on exotic and non-compliant exchange platforms.
How to store ETC tokens?
To store Ether Classic, as with storing any other type of cryptocurrency, you need to use what is called a cryptocurrency wallet. Wallets are essential and indispensable tools when investing in cryptocurrency because the security of your investment is partly guaranteed by them. Cryptocurrency wallets allow users to interact with the blockchain and thus be able to transfer, examine, and receive cryptocurrency.
Each wallet has its own wallet address that makes it possible to send and receive tokens, and each wallet address has a public and a private key:
The public key is mathematically linked to the hash function and the private key allows access to the funds linked to a wallet address, just as a password allows access to the money in a bank account.
The different cryptocurrency wallets
It is important to learn about the different types of wallets before getting one to store your funds in. Depending on the needs of the individual, but also in relation to risk factors, some types of wallets will be more suitable for their purpose than others. Here are the types of cryptocurrency wallets that exist:
- Web wallet: or online wallet is provided by crypto exchange platforms and brokers for storing crypto currencies. It allows you to access your funds and sell, exchange or receive funds through any browser connected to the internet. Its main advantage is the comfort it grants to its users through its ease of access, but on the other hand, its security level is very low because the providers of this service mostly hold the keys instead of the wallet owners.
- Mobile wallet: an application that must be downloaded on smartphones and other mobile devices. More suitable for everyday spending, it allows you to access your wallet directly on your devices but also to use your cryptoassets to make purchases in places where payments via cryptocurrencies are allowed. This type of wallet offers additional protection especially with the password that unlocks the devices. The risk with the mobile wallet is the risk of having your device stolen, in which case you would no longer be able to access your wallet and you would be a victim of theft of your tokens as well as your personal information if they managed to hack and unlock the device.
- Desktop wallet: a software or program to be installed on your computer. It offers much more security than online wallets (web wallets) thanks to the multi-factor identification (MFA or 2FA). Nevertheless, it can still be the target of viruses whose aim is data theft and hacking by hackers. Therefore, to reduce this risk, it is necessary to install an anti-virus and to store the data recovery phrase on another device.
- Hardware wallet: the hardware wallet is a highly encrypted physical device not connected to the internet that stores the different keys of an address and makes them almost untouchable. In terms of security, it far exceeds any other type of wallet.
- The paper wallet: is only a wallet in name because it is a simple sheet of paper where the wallet address and the different public and private keys are written. It is impossible to be hacked with this method but the disadvantage is that it is only necessary to get your hands on this sheet of paper to have in your possession all the information and elements necessary to access and use the wallet of an individual.
To store Classic Ether, here are the best wallets:
Guarda wallet, Cobo, trust wallet, Atomic wallet (mobile wallets)
Coinnomi, Emerald wallet, Jaxx liberty (desktop wallets)
Ledger Nano, Trezor, SafePal, Party sign (hardware wallets)
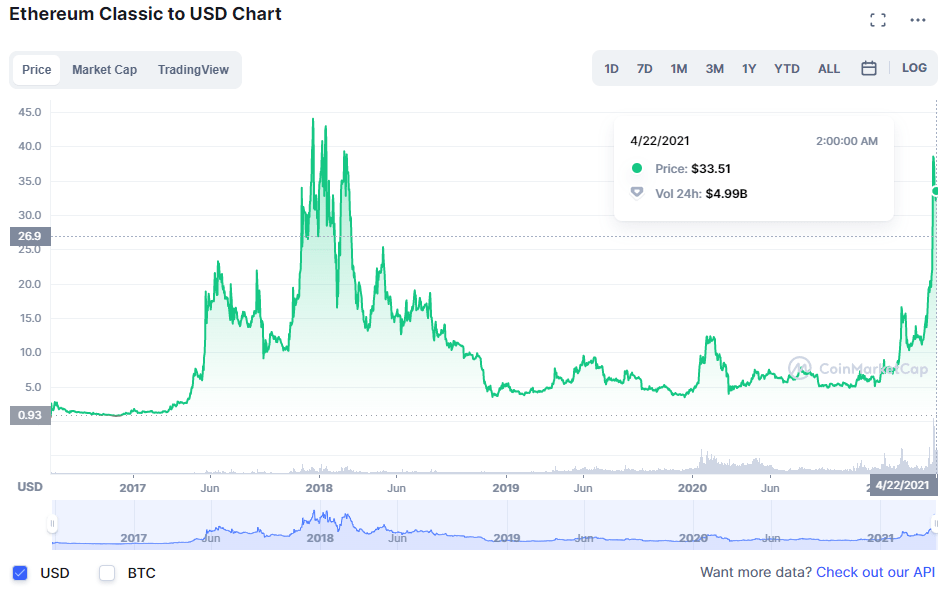
History and current price of Ether Classic
The price of Ether Classic like any other cryptocurrency is influenced by supply and demand in the market. It is therefore not possible to give a precise value as it fluctuates every second. At the time of writing, Ether Classic has a value of $27.9 with a change of -4.91% and an exchange volume of $4,272,837,497 over a 24 hour period.
2016
At the launch of the Ethereum fork, Ethereum Classic, the price was quoted at 0.6 dollars and rebounded two days later to 215 dollars. It then suffered a drop to 1.43 dollars but managed to recover to around 3.27 dollars. However, after September, the price kept falling and having insignificant rises. Its value then stagnated below 1 dollar for 3 months.
2017
At the beginning of the year, the ETC price reached 1.5 dollars and then lost value and fell below 1 dollar. It managed to rise to 1.4 dollars in February and continued its evolution reaching about 10 dollars per token. For 5 consecutive months, from May to September, the ETC stayed above 10 dollars and then fell below and ended the year with a record value of 34.17 dollars.
2018
It was in 2018 that Ether Classic experienced its historic price of 42.96 dollars.
2019
The price of Ether Classic underwent a decrease and ended up varying between 3 and 10 dollars.
2020
The price of ETC has fluctuated between 3.96 dollars and 12.34 dollars during this year but has mostly stabilized at around 5 and 6 dollars.
What is the future for Ethereum Classic and its cryptocurrency?
The problem with Ethereum Classic is that it cannot maintain a trend over a long period of time. The company is currently in a period of regeneration and reorganization. Developers are working to ensure that the security level of the network is constantly improving. Especially with the updates and development of the Proof of Work system. Ethereum Classic certainly does not have the same level and speed of development as its twin Ethereum, and is in fact far behind it in terms of token value, but it continues to evolve at its own pace despite the many hacks, competitors and speculations.
In view of all these elements, moderate investments in this cryptocurrency are worth considering. Nevertheless, the progressions of Ether Classic are indeed very slow, but they have the merit of being safe. Ether Classic promises to be subject to great developments in the years to come if the company manages to increase its human and technological resources but also to equip itself with a robust and reliable enough security system so that it is not one of the reasons why investors turn away from this cryptocurrency.